Arrays in Java
What are
Java Array?
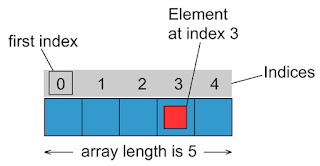
Array is an
Indexed Collection of
Fixed Number of
Homogeneous/Similar Data Elements.
int[ ] x = new int[5];
Example:
Valid Array Examples:
int[ ] arr1=new
int[5];
int arr2[ ]=new
int[5];
int [ ]arr3=new
int[5];
int[ ] arr4 = new
int[ ]{10,20,30,40,50};
int[ ] arr5 =
{10,20,30,40,50};
Arrays can be
initialized when they are declared. The array will automatically be
created large enough to hold the number of elements you specify in the array
initializer. There is no need to use new.
public
static void main(String args[]) {
int
month_days[ ];
month_days
= new int[12];
month_days[0]
= 31;
month_days[1]
= 28;
month_days[2]
= 31;
month_days[3]
= 30;
month_days[4]
= 31;
month_days[5]
= 30;
month_days[6]
= 31;
month_days[8]
= 30;
month_days[9]
= 31;
month_days[10]
= 30;
month_days[11]
= 31;
System.out.println("April
has " + month_days[3] + " days.");
}
}
Advantage of Java Array
1. Code Optimization: It makes the code optimized, we can retrieve or sort the data easily.
2. Random access: We can get any data located at any index position.
Disadvantage of Java Array
1. Size is fixed(Static Array): We can store only fixed size of elements in the array. It doesn't grow its size at runtime. To solve this problem, collection(Dynamic Array) framework is used in java.
2. Similar Data Type: To solve this problem, we use Object Array.
class
TestArray{
public static void
main(String args[]){
//1. int array:
int a[ ]=new
int[5]; //declaration and
instantiation
a[0]=10; //initialization
a[1]=20;
a[2]=30;
a[3]=40;
a[4]=50;
System.out.println(a.getClass().getName()); //Corresponding class name
System.out.println(a.length); //size or length of array
//print all the
values of array: use for loop
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){//length
is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
//2. double array:
double d[ ]=new
double[3];
d[0]=10.12;
d[1]=11.22;
d[2]=45.86;
//3. char array:
char c[ ]=new
char[3];
c[0]='a';
c[1]='7';
c[2]='$';
//4. boolean array:
boolean b[ ]=new
boolean[2];
b[0]=true;
b[1]=false;
//5. String array:
String s[ ]=new
String[2];
s[0]="Hello";
s[1]="World";
//6. Object array: (Object is a class) --> used to store different data types
values.
Object ob[ ]=new
Object[7];
ob[0]="Navdeep";
ob[1]=28;
ob[2]=17.23;
ob[3]="India";
ob[4]=true;
ob[5]='M';
ob[6]="01/01/2018";
}}
ARRAY
Creation:
Every Array in
Java is an Object only. Hence, we can create Arrays by using new operator.
Ex:
int[ ] a=new
int[3];
For every Array type corresponding classes
are available and these classes are part of Java Language and not available to
the programmer level.
Ex:
int[ ] a=new
int[3];
System.out.println(.getClass().getName()); [I
Array Type
|
Corresponding Class Name
|
int[
]
|
[I
|
int[
][ ]
|
[[I
|
byte[
]
|
[B
|
short[
]
|
[S
|
long[
]
|
[J
|
float[
]
|
[F
|
double[
]
|
[D
|
char[
]
|
[C
|
boolean[
]
|
[Z
|
String[
]
|
[Ljava.lang.String;
|
String[
][ ]
|
[[Ljava.lang.String;
|
Object[
]
|
[Ljava.lang.Object;
|
Object[
][ ]
|
[[Ljava.lang.Object;
|
Loopholes
in Array Creation:
1) At the time of
Array creation compulsory we should specify the size, otherwise we will get
compile time error.
int[ ] x = new
int[ ]; //Invalid
int[ ] x = new
int[6]; //Valid
2) It is legal to
have an array with size 0 in java.
int[ ] x = new
int[0];
public static void
main(String[ ] args)
Sopln(args.length);
//Output: 0
3) If we are
trying to specify array size with some Negative int value then we will get
Runtime Exception saying “NegativeArraySizeException”
int[ ] x = new
int[-6];
4) If we are
trying to initialize more than array size then we will get Runtime Exception
saying “ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException”
int[ ] x = new
int[4];
x[4] = 200; //“ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException”
5) To specify
Array size allowed Data types are:
byte, short, char
and int.
If we are trying
to specify any other types then we will get Compile Time Error.
int[ ] x = new
int[10];
int[ ] x = new
int[‘a’];
byte b = 20;
int[ ] x = new
int[b];
short s = 40
int[ ] x = new
int[s];
6) The maximum
allowed Array size in java is 2147483647 which is the maximum value of int data
type.
int[ ] x = new
int[2147483647]; Valid {We get Runtime exception if sufficient heap
memory not available}
int[ ] x = new
int[2147483648]; {CE: int number too large}
Passing Java
Array to a Method
We can also pass arrays to methods just as
we can pass primitive type values to methods.
Example:-
public class
ArrayMethods{
public static void
main(String args[])
{
int x[ ] = { 1, 2, 3 };
data(x);
}
public static void
data(int y[ ])
{
System.out.println(y[0]);
System.out.println(y[1]);
System.out.println(y[2]);
}
}
Multidimensional
Array(arrays of arrays)
These
are other Multidimensional arrays representation of other data types.
The main Advantage
of this Multidimensional arrays is Memory
Utilisation will be improved.
Array
Declaration
1. One Dimensional Array Declaration
int[ ] x; //This one is Recommended because variable is
clearly separated from the data type.
int [ ]x; //Valid
int x[ ]; //Valid
Ø
At the
time of Declaration we can’t specify the size, else we will get Compile Time
Error.
int[6]
x; //Invalid
int[
] x; //Valid
2. Two Dimensional Array Declaration
int[ ][ ] x;
int [ ][ ]x;
int x[ ][ ];
int[ ] [ ]x;
int[ ] x[ ];
int [ ]x[ ];
All above are
Valid Declaration.
Question: Which of the following are valid?
1. int[ ] a,b;
2. int[ ] a[ ],b;
3. int[ ] a[ ],b[
];
4. int[ ] [ ]a,b;
5. int[ ] [ ]a,b[
];
6. int[ ] [ ]a,[
]b;
Ans: 1 to 5 are Valid, 6 is Invalid.
Explanation:-
1. a - 1, b - 1
2. a - 2, b - 1
3. a - 2, b - 2
4. a - 2, b - 2
5. a - 2, b - 3
6. Compile time
Error
Conclusion:
1. If we want to
dimension before the variable that facility is applicable only for 1st
variable in a declaration.
2. If we are
trying to apply for next variable or remaining variables we will get Compile
time Error.
int[ ] [ ]a, [ ]b, [ ]c;
Here only [ ]a is
Valid
[ ]b, [ ]c is
Invalid.
3. Three-Dimensional Array Declaration
int[ ][ ][ ] a;
int [ ][ ][ ]a;
int a[ ][ ][ ] ;
int[ ] [ ][ ]a;
int[ ] a[ ][ ];
int[ ] [ ]a[ ];
int[ ][ ] [ ]a;
int[ ][ ] a[ ];
int [ ][ ]a[ ];
int [ ]a[ ][ ];
All above are
Valid Declaration.
Question: Which of the following array
declarations are Invalid?
1. int[ ] a = new
int[ ];
2. int[ ] a = new
int[3];
3. int[ ][ ] a =
new int[ ][ ];
4. int[ ][ ] a =
new int[3][ ];
5. int[ ][ ] a =
new int[ ][4];
6. int[ ][ ] a =
new int[3][4];
7. int[ ][ ][ ] a
= new int[3][4][5];
8. int[ ][ ][ ] a
= new int[3][4][ ];
9. int[ ][ ][ ] a
= new int[3][ ][5];
10. int[ ][ ][ ] a
= new int[ ][4][5];
Answer: 1, 3, 5, 9, 10 are Invalid
At least base size
we must specify.
Array
Once we create an
Array every array element by default initialised with default values.
Example 1:
int[ ] x = new
int[3];
Sopln(x); Output: [I@3e25a5
Sopln(x[0]); Output: 0
Note: Whenever we are trying to print any reference variable,
internally 2 string method will be called which is implemented by default to
return the string in the following form “classname@hashcode_in_hexadecimalform”.
Example 2:
int[ ][ ] x = new
int[2][3];
Sopln(x); Output: [[I@3e25a5
Sopln(x[0]); Output: [I@19821f
Sopln(x[0][0]); Output: 0
Example 3:
int[ ][ ] x = new
int[2][ ];
Sopln(x); Output: [[I@3e25a5
Sopln(x[0]); Output: null
Sopln(x[0][0]); Output: Runtime Exception: NullPointerException
Note: If we are trying to perform any operation on null then we
will get runtime exception saying “NullPointerException”.
Once we create an
Array, every array element by default initialised with default values. If we
are not satisfied with default values then we can override these values with
our customised values.
int[ ] x = new
int[6];
x[0] = 10;
x[1] = 20;
x[2] = 30;
x[3] = 40;
x[4] = 50;
x[5] = 60;
Invalid
scenarios for above example:
x[6] = 70; {Runtime Exception:
ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException;}
x[-6] = 80; {Runtime Exception:
ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException;}
x[2.5] = 90; {CE: Possible Loss of Precision, Found:
Double; Required: int}
Note: If we are trying to access Array element with out of range
index (Either positive value or Negative int value) then we will get runtime
exception saying “ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException”.
Array
Declaration, Creation and Initialisation in a single line
We can Declare,
Create and Initialise an Array in a single line (Shortcut representation).
int[ ] x;
x = new int[3];
x[0] = 10;
x[1] = 20;
x[2] = 30;
OR
int[ ] x = {10, 20, 30};
other data types
as well can be represented in a single like
char[ ] ch = {‘a’,
‘e’, ‘i’};
string[ ] s =
{“nick”, “nav”, “java”};
We can use this shortcut representation for
multidimensional arrays also.
int[ ][ ] x = {{10, 20}, {30,
40, 50}};
Example:
int[
][ ][ ] x = {{{10, 20, 30}, {40, 50, 60}},{{70, 80}, {90, 100, 110}}};
1.
Sopln(x[0][1][2]); Output:
60
2.
Sopln(x[1][0][1]); Output:
80
3.
Sopln(x[2][0][0]); Output:
RE: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
4.
Sopln(x[1][2][0]); Output:
RE: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
5.
Sopln(x[1][1][1]); Output:
100
6.
Sopln(x[2][1][0]); Output:
RE: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
Conclusion:
If
we want to use this shortcut, compulsory we should perform all activities in a
single line.
If
we are trying to divide into multiple lines then we will get Compile Time
Error.
int[
] x = {10, 20, 30};
int[
] x;
x=
{10, 20, 30}; Compile Time Error: Illegal start of
expression.
length vs length()
length:
length
is a final variable applicable for arrays.
length
variable represents the size of the array.
Example:
int[
] x = new int[6];
Sopln(x.length()); Output: CE: Can’t find symbol, symbol:
method length(), location: class int[ ]
Sopln(x.length); Output: 6
Length():
length()
method is a final method applicable for string objects.
length()
method returns number of characters present in the string.
string
s = “noddy”
Sopln(s.length); Output: CE: Can’t find symbol, symbol:
variable length, location: class j.l.String
Sopln(s.length()); Output: 5
NOTE:
Ø length variable applicable for arrays but
not for string objects.
Ø length() method applicable for string
objects but not for arrays.
Question: String[ ] s = {“A”, “XX”, “ABC”};
1.
Sopln(s.length); Output: 3
2.
Sopln(s.length()); Output: CE: Can’t
find symbol, Symbol: method length(), location: class String[ ]
3.
Sopln(s[0].length); Output: CE: Can’t
find symbol, Symbol: variable length, location: class j.l.String
4.
Sopln(s[0].length()); Output: 1
Note: In multidimensional array length variable
represents only base size but not total size.
int[
][ ] x = new int[6][3];
Sopln(x.length);
Output: 6 //row
Sopln(x[0].length);
Output: 3 //column
Note: There is no direct way to find total
length of multidimensional array but indirectly we can find as follows
X[0].length + X[1].length +
X[2].length + X[3].length …….
Anonymous Array
Sometimes
we can declare an array without a name, such type of nameless arrays is called
anonymous arrays.
The
main purpose of anonymous arrays is just for instant use. (One-time usage)
We can create anonymous array
as follows:
new int[ ] {10, 20, 30, 40}
While
creating anonymous array we can’t specify the size. Otherwise we will get
compile time error
new
int[3] {10, 20, 30, 40} //Invalid
new
int[ ] {10, 20, 30, 40} //Valid
We
can create multidimensional anonymous array also.
new int[ ][ ] {{10, 20}, {30,
40, 50}}
Based
on our requirement we can give the name for anonymous array then it is no
longer anonymous.
int[
] x = new int[ ] {10, 20, 30};














java language with basic samples
ReplyDeleteGetting x and y positions of JFrame